
The digital age has ushered in a new era of marketing and brand representation, with social media influencers becoming pivotal in shaping consumer preferences
Gone are the days of human fashion influencers.
Enter virtual models.
The digital age has ushered in a new era of marketing and brand representation, with social media influencers becoming pivotal in shaping consumer preferences.
However, a new trend is emerging that poses a unique challenge to human influencers: the rise of virtual models.
These AI-generated personas are gaining popularity, offering brands a cost-effective and controlled alternative to traditional influencer partnerships.
Virtual models are computer-generated characters that mimic the roles of human influencers.
They are designed to engage with real audiences on social media platforms, promoting products, and creating content just as their human counterparts do.
The concept isn’t entirely new; virtual characters like Barbie have long had a presence online.

However, the sophistication of these models has increased significantly, blurring the lines between virtual and reality.
The creation of virtual models is a sophisticated blend of art and science, powered by cutting-edge advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and graphics design.
AI technologies like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and deep learning algorithms are at the forefront, enabling the generation of hyper-realistic virtual models that can be used for advertising, fashion shows, and promotional materials.
These models are crafted with meticulous attention to detail, simulating human-like expressions and movements that were once thought impossible
The history of virtual influencers dates back further than one might expect, with roots in various forms of media and entertainment.
The concept of fictional characters achieving fame and influence can be traced back to the 1930s with Cynthia the “Gaba Girl”, a lifelike mannequin created by sculptor Lester Gaba for Saks Fifth Avenue.

Cynthia became a media sensation, receiving fan mail and even attending high-profile events.
In the realm of digital media, Max Headroom is often cited as one of the first virtual influencers.

Introduced in 1985, Max was a fictional AI character with a distinctive electronic voice and glitchy video-edit style, becoming a pop culture icon and hosting his own TV show.
The Japanese anime and idol culture of the 1980s gave rise to virtual idols, with Lynn Minmay from the anime series “Super Dimension Fortress Macross” (1982) being one of the earliest examples.
She was a fictional singer whose success paved the way for more virtual idols like EVE from “Megazone 23” (1985)

and Sharon Apple in “Macross Plus” (1994).

The evolution of virtual influencers continued with the advent of Vocaloids like Hatsune Miku, who debuted in 2007 and became a global phenomenon, performing at live concerts with a holographic presence and amassing a huge fanbase.

The rise of VTubers (virtual YouTubers) further expanded the landscape, with characters like Kizuna AI gaining popularity for their engaging content and interactive capabilities.

Today, virtual influencers are a growing trend, with advancements in AI and motion capture technology allowing for more realistic and relatable digital personalities.
They collaborate with brands, release music, and engage with social issues, demonstrating the potential for virtual entities to have a significant impact on culture and marketing.
The success of virtual influencers like Lil Miquela and Aitana Lopez highlights the ongoing evolution and influence of these digital creations in the modern world.
One of the most prominent virtual models is Lil Miquela, a CGI creation with over 2.6 million followers on Instagram and 3.5 million on TikTok.
Lil Miquela, also known as Miquela Sousa, is a trailblazer in the realm of virtual influencers. She represents a new era of digital personalities.
Created by the Los Angeles-based startup Brud, Lil Miquela is a 19-year-old half-Spanish, half-Brazilian model who resides in LA.
She has been named one of the 25 most influential people on the internet by TIME magazine in 2018, alongside celebrities like BTS and Rihanna.
Her collaborations extend beyond BMW to include other luxury brands such as Prada, Dior, and Calvin Klein, and she has even released music, with her single “Not Mine” debuting in 2017.
Lil Miquela’s influence is not just limited to fashion and entertainment; she also engages with her audience on human rights and social causes, adding depth to her virtual persona.
She has collaborated with luxury car manufacturer BMW, showcasing the brand’s innovative spirit and appeal to a tech-savvy audience.

Aitana Lopez is a virtual influencer with more than 300,000 followers, created by The Clueless, an AI modeling agency based in Barcelona.
She is described as a 25-year-old exuberant fitness enthusiast from Barcelona, with a complex character and vibrant pink hair.
Aitana’s presence is felt across social media, where she earns over ₹91,000 per advertisement and has a monthly average income of approximately ₹2.73 lakh.
The Clueless Agency, which also created Aitana, is known for its innovative approach to AI modeling and influencer marketing, crafting stories and personalities that resonate with audiences globally.
Aitana’s success is a testament to the agency’s ability to blend art, technology, and business acumen to create a compelling digital narrative.
Here’s a listicle of the top 10 virtual models on social media, each with their unique charm and influence:

2. Lil Miquela: This virtual robot model from the USA has collaborated with top fashion brands like Prada, Dior, and Calvin Klein. With millions of followers, she’s also ventured into music, adding another dimension to her digital persona.

3. Barbie: The iconic doll has successfully transitioned into the digital age, becoming a social media influencer who inspires with her timeless style and empowering messages.

4. Guggimon: Known for his edgy fashion sense and bold personality, Guggimon is a virtual model that brings a unique flair to the influencer world.

5. Any Malu: This animated character from Brazil charms her audience with her vibrant personality and engaging content.

6. Anna Cattish: Anna’s distinct style and artistic vibe resonate with her followers, making her a standout virtual model.

7. Thalasya: Indonesia’s very own virtual model, Thalasya, captivates with her stunning visuals and cultural representation.

8. Janky: Janky’s quirky and unconventional style sets him apart in the virtual influencer space.

9. Noonoouri: With her high-fashion looks and advocacy for social issues, Noonoouri has carved out a significant presence online.

10. bee_nfluencer: Originating from France, this virtual bee influencer buzzes with a mission to save real bees, combining influencer marketing with environmental activism.

These virtual models are redefining the boundaries of social media influence and opening up new possibilities for brand collaborations and storytelling.
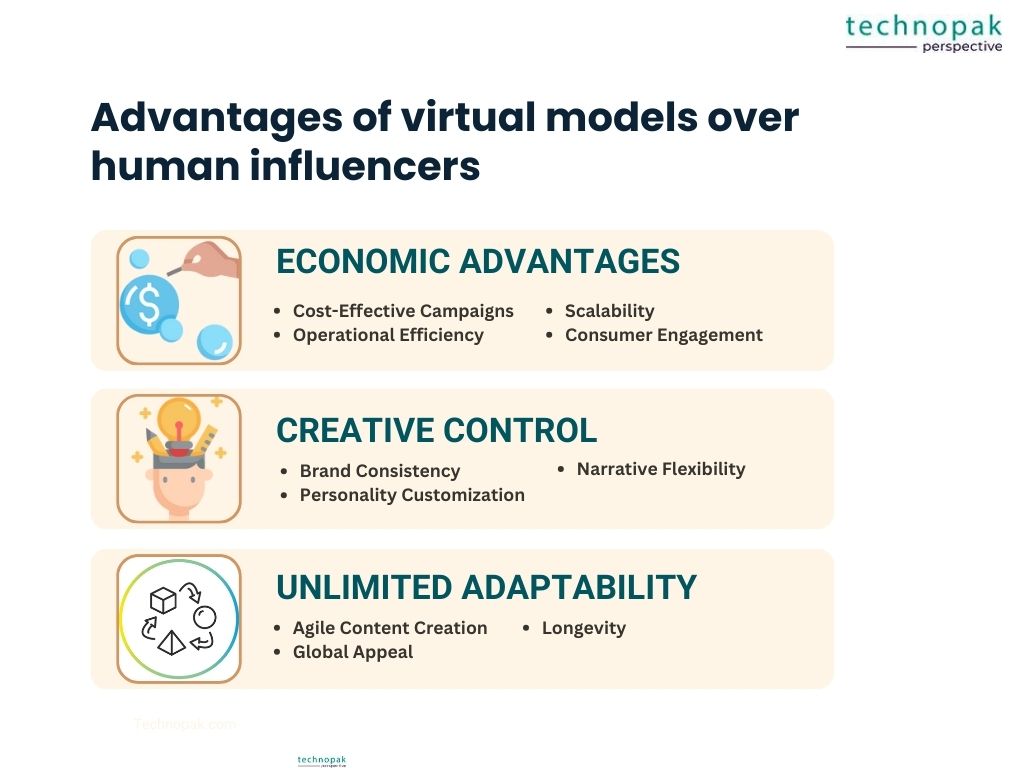
The Economic Advantages of leveraging these digital influencers are multifaceted, encompassing cost-effectiveness, operational efficiency, and scalability.
Let’s explore the economic incentives that are driving brands towards this innovative frontier.
The advent of virtual models has not only disrupted the economic framework of influencer marketing but also bestowed brands with unprecedented Creative Control.
This transformative power allows brands to meticulously sculpt every facet of their digital ambassadors, from their visual appearance to their personality traits.
The creative liberties afforded by virtual models are redefining the essence of brand storytelling in the digital age.
The digital era has ushered in a paradigm where adaptability is key to staying relevant, and virtual models are the epitome of this principle.
Under the advantage umbrella of Unlimited Adaptability, these digital entities offer brands the agility to pivot and tailor content swiftly to meet the ever-changing demands of the market.
In essence, virtual models provide a cost-efficient, creatively liberating, and adaptable solution for brands looking to innovate in the digital marketing arena. They represent a shift towards a more controlled, strategic approach to influencer marketing that can yield significant returns on investment.
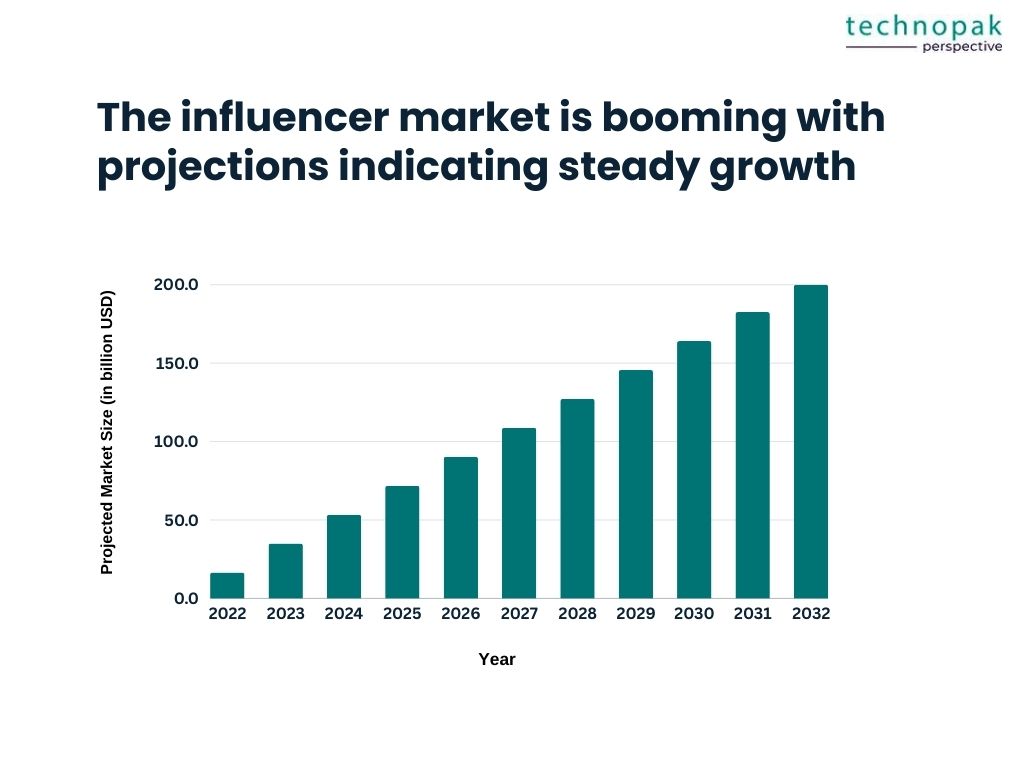
The influencer market is booming, with projections indicating growth from $16.5 billion in 2022 to nearly $200 billion by 2032.
A survey by Forbes in the US revealed that 58% of respondents follow at least one virtual influencer, and 35% have purchased a product promoted by one.
Virtual influencers are capitalizing on this trend, with notable figures getting to work with major brands like BMW.
Despite initial skepticism, the public, particularly the younger lot, has shown a willingness to engage with virtual influencers.
Echoing this sentiment, Sprout Social has revealed acceptance of virtual influencers is particularly strong among younger, tech-savvy audiences who are more open to digital innovations.
According to Springer, nearly 75% of American consumers aged between 18 and 24 follow at least one virtual influencer. Among respondents aged between 25 and 44, 67% expressed engagement with virtual influencers.
The same survey revealed that 35% of consumers have purchased a product promoted by a virtual influencer. The age group most likely to have made such a purchase is 18-44.
Brands partnering with virtual influencers can maintain absolute control over projects from conception to completion.
They offer a novel form of entertainment and interaction, akin to following a character in a television series.
This acceptance is particularly strong among younger, tech-savvy audiences who are often more open to digital innovations.
The influence of virtual models on audiences extends beyond mere aesthetics; it delves into the psychological realm.
Virtual influencers can shape perceptions of beauty, fashion, and lifestyle, potentially impacting self-image and identity.
Studies have shown that the presence of an audience can affect the appeal of virtual reality experiences, with extroverts being less anxious about trying VR in front of others compared to introverts.
For instance, a study was recently conducted by researchers from Royal Holloway, University of London.
The study, titled “The Impact of an Audience on the Appeal of Virtual Reality,” found that individuals trying virtual reality in front of others rated the experience as more anxiety-provoking than when there was no audience present.
Moreover, the study revealed that extroverted individuals were less affected by the size of the audience in terms of anxiety compared to introverts.
These findings suggest that personality traits such as extroversion can influence one’s willingness to engage with virtual reality in public settings.
The rise of virtual models brings forth ethical debates concerning the authenticity of their interactions and the potential for misleading audiences.
Questions arise about the moral implications of creating virtual experiences that closely mimic reality and the impact on employment for human models.
Ethical guidelines and moral responsibilities are becoming increasingly important as designers create and develop complex interactive virtual worlds.
Virtual models are not confined by geography, allowing them to have a global presence.
For instance, Lu Do Magalu from Brazil has 6 million Instagram followers,
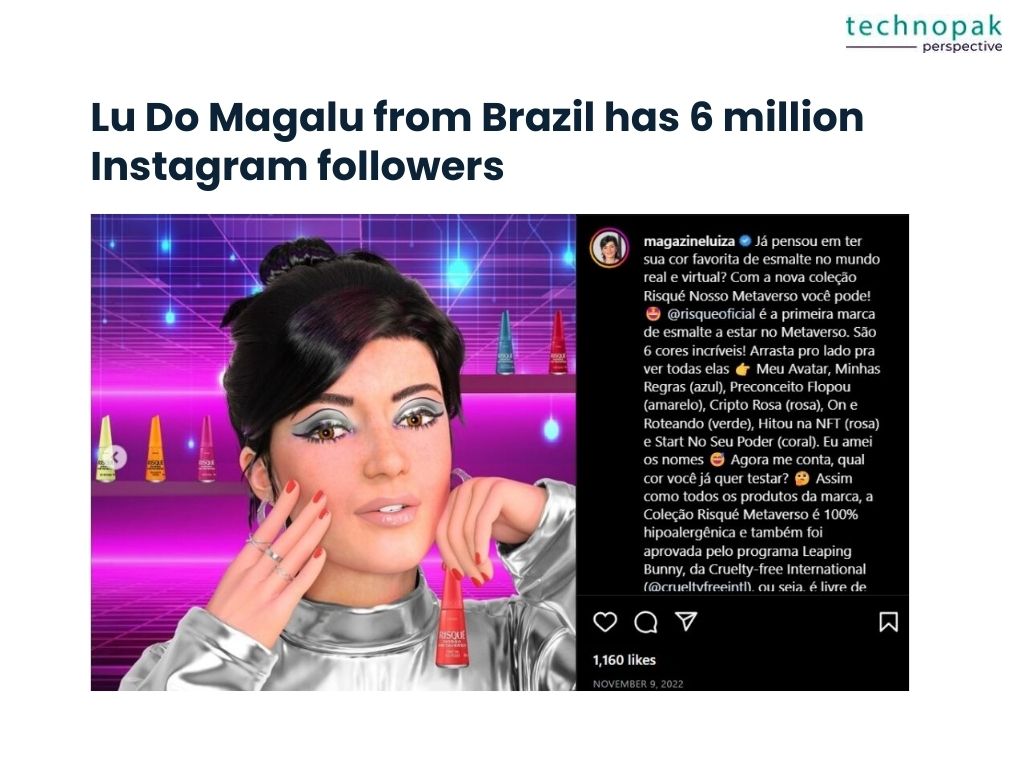
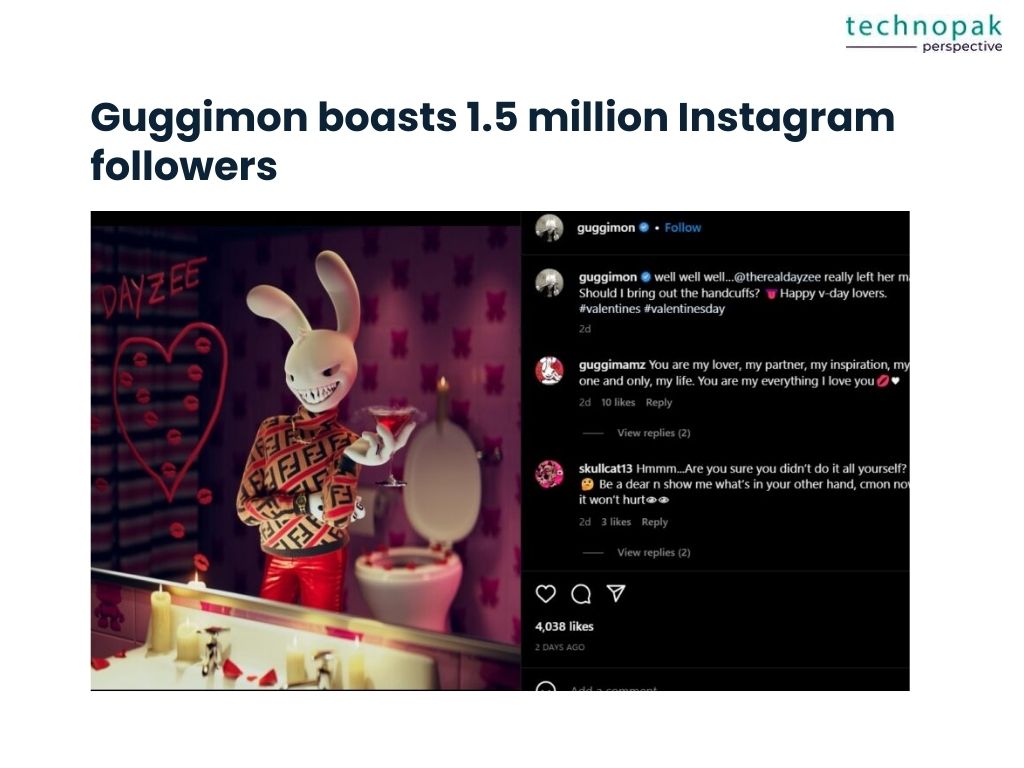
while Guggimon boasts 1.5 million Instagram followers, demonstrating the worldwide reach and influence of these digital creations.
Lu Do Magalu, hailing from Brazil, is not just a virtual influencer but a symbol of modern marketing and digital interaction.
With a staggering following of over 25 million across social media platforms, Lu represents Magazine Luiza, one of Brazil’s largest retail companies.
She engages her audience with unboxing videos, product reviews, and software tips, all while advocating for social causes like domestic abuse awareness and LGBT rights.
Her presence extends beyond Instagram, influencing through Facebook and YouTube, making her a versatile digital icon.
On the other hand, Guggimon is a virtual influencer with a flair for the dramatic, known for his edgy style and horror obsession.
Originating from Montreal, Canada, Guggimon is a creation of Superplastic, a company specializing in animated synthetic celebrities and designer toys.
With 1.4 million followers on Instagram, he stands out for his collaborations with major brands like Gucci and his appearance as a playable character in Fortnite.
Guggimon’s persona is a blend of fashion, horror, and music, resonating with fans who appreciate his unique mixtape productions and quirky social media presence.
Here are more examples that highlight the international diversity of virtual models:

These virtual models from different parts of the world not only represent the diversity in the digital space but also illustrate how brands can leverage this technology to reach a broader audience.
They are changing the landscape of marketing and social media influence by transcending physical and cultural barriers, allowing for a truly global presence.
With their ability to generate significant engagement and offer creative flexibility, they are set to become an integral part of the marketing mix for brands around the world.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect virtual influencers to become even more prevalent.
They offer a glimpse into the future of marketing, where AI and creativity merge to create compelling narratives that resonate with a digital audience.
While human influencers will undoubtedly remain relevant, they will need to adapt and innovate to stay competitive in this evolving landscape.
In conclusion, virtual models represent a significant shift in the influencer marketing domain.
They offer brands a new avenue for engagement, while also challenging human influencers to elevate their content to meet changing consumer expectations.
As we move forward, the interplay between human creativity and AI will shape the future of social media marketing.

Looking for futuristic solutions to amp up your fashion business? Trust Technopak with its Animeta and CGS tools to help you ascend.