Lab grown diamonds are diamonds that are created in a laboratory using advanced technology, rather than mined from the earth.
They have the same physical, chemical and optical properties as natural diamonds, but with some key advantages: they are more affordable, more ethical and more environmentally friendly.
Technopak with its pulse on major trends in retail, fashion and beauty, delves into the latest trend catching the fancy of consumers.
Thus, in this blog post, we will explore how lab grown diamonds are transforming India’s diamond industry, which is already a global leader in the cutting and polishing of natural diamonds.
We will also look at the lab grown diamond jewellery as its stands in numbers across India and the world.
Lab grown diamonds are also known as synthetic diamonds or cultured diamonds.
They are made by replicating the natural process of diamond formation, which involves exposing carbon atoms to high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) or to a carbon-rich gas in a sealed chamber (CVD).
The result is a rough diamond that can be cut and polished into various shapes and sizes, just like a natural diamond. Lab grown diamonds can also be coloured or enhanced to create different hues and effects.
CVD and HPHT are two methods of producing lab grown diamonds, which are diamonds that are created in a laboratory using advanced technology, rather than mined from the earth.
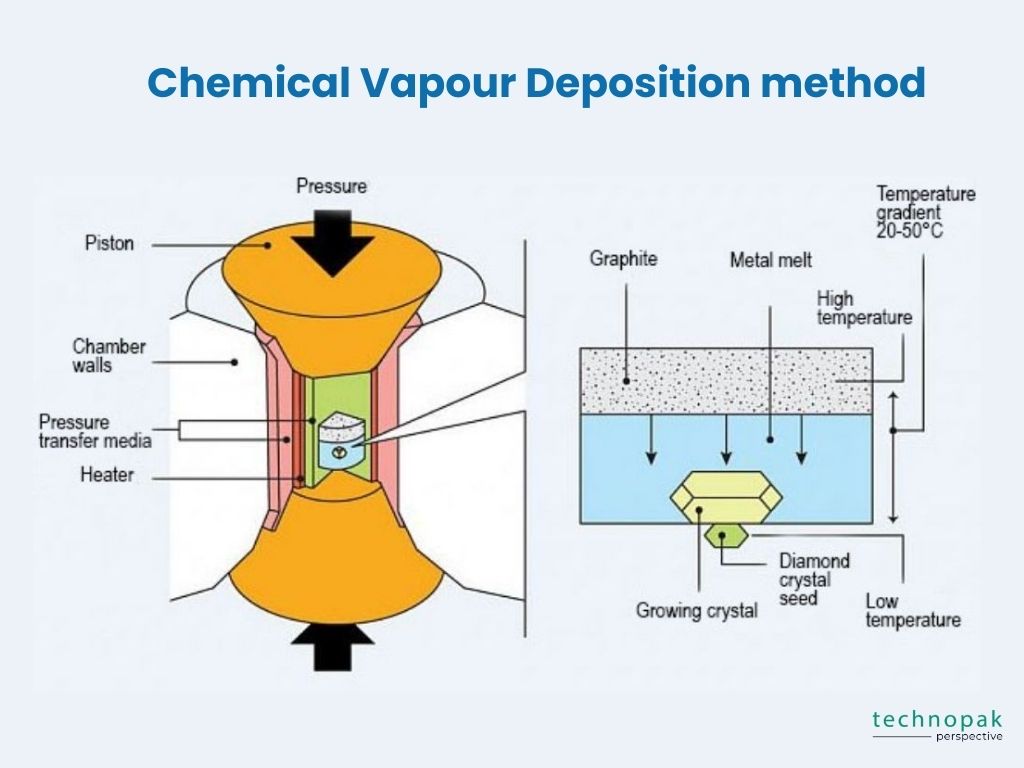
CVD stands for chemical vapor deposition, which is a process that involves exposing a small diamond seed to a carbon-rich gas in a sealed chamber.
The gas is heated to very high temperatures, causing the carbon atoms to break down and deposit on the diamond seed, forming a larger diamond crystal.
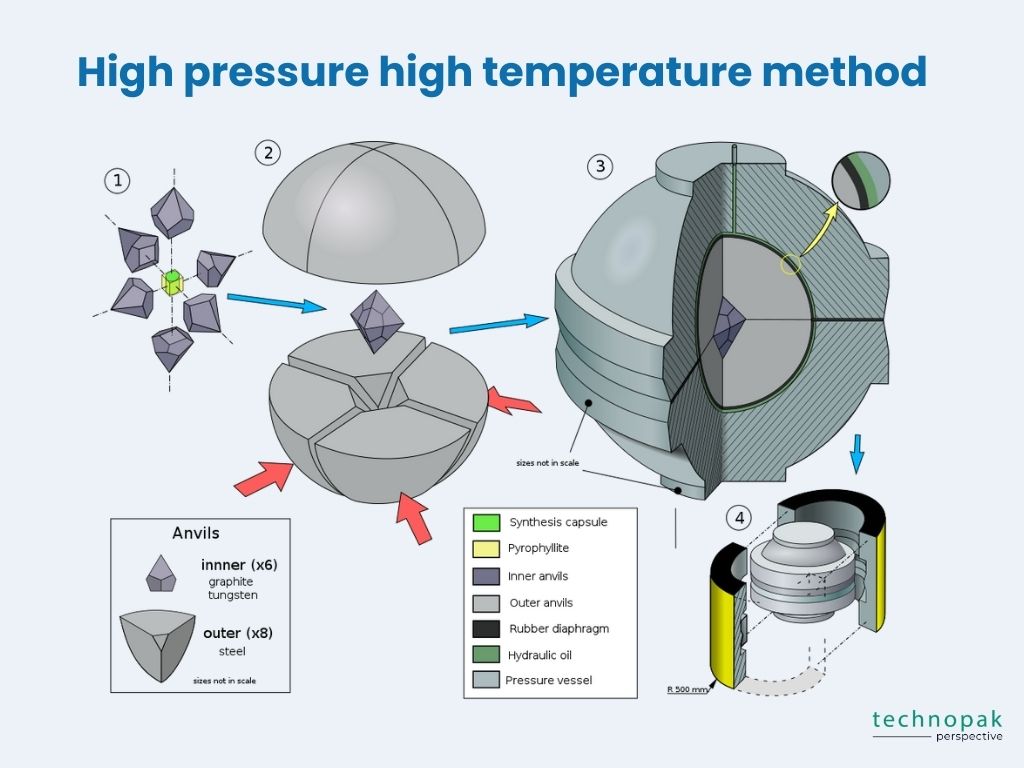
HPHT stands for high pressure high temperature, which is a process that involves subjecting a diamond seed to extremely high pressure and temperature in a special device.
The pressure and temperature conditions mimic those found in the earth’s mantle, where natural diamonds are formed. The diamond seed grows into a larger diamond crystal under these conditions.
Both CVD and HPHT produce diamonds with the same physical, chemical and optical properties as natural diamonds, but they have some differences in terms of cost, color, quality and shape.
For example, CVD diamonds tend to be cheaper, more colorless, more pure and more cubic than HPHT diamonds, which tend to be more expensive, more colored, more included and more cuboctahedral.
However, these differences are not absolute, and both methods can produce a variety of diamonds with different characteristics.
Conventional or normal diamonds are diamonds that are mined from the earth, rather than created in a laboratory.
They are formed when carbon atoms are exposed to extremely high pressure and temperature deep in the earth’s mantle, causing them to bond into a rigid crystal structure.
This process can take billions of years, and the resulting diamonds are then brought to the surface by volcanic eruptions or erosion.
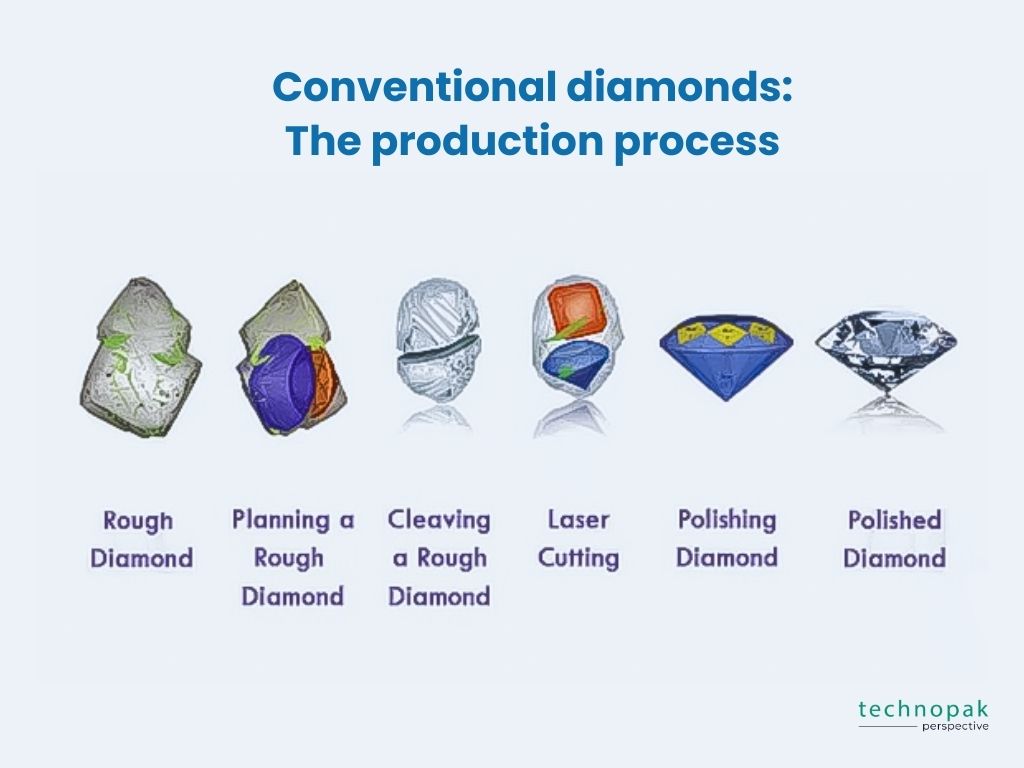
Here’s the process in steps:
The most prevalent way diamonds are created is by volcanic blasts that rise from the earth’s mantle in a kimberlite eruption (a small yet powerful volcanic explosion caused by the quick ascent of kimberlites). Diamonds require a lot of pressure and heat to form, and the mantle has high temperatures and the pressure of about 100 miles of rock above it. Diamonds can also be made by an asteroid impact due to the high temperatures and pressures that these collisions generate on the Earth’s surface. Diamonds have also been discovered in meteorites that landed on the Earth from space, but these diamonds are usually smaller than the others.
But how does a rough diamond deep in the Earth become the most dazzling stone?
Before a rough diamond becomes a stunning piece of jewellery, it has to go through several steps in its production.
As of 2024, the global diamond industry has undergone significant changes, with natural diamond mining output declining to approximately 105 million carats, marking the lowest volume since 1995 due to aging mines and reduced demand. In contrast, lab-grown diamonds now account for 14.3% of the total diamond supply, with the global market valued at $25.68 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $28.27 billion by 2025 at a 10.1% CAGR.
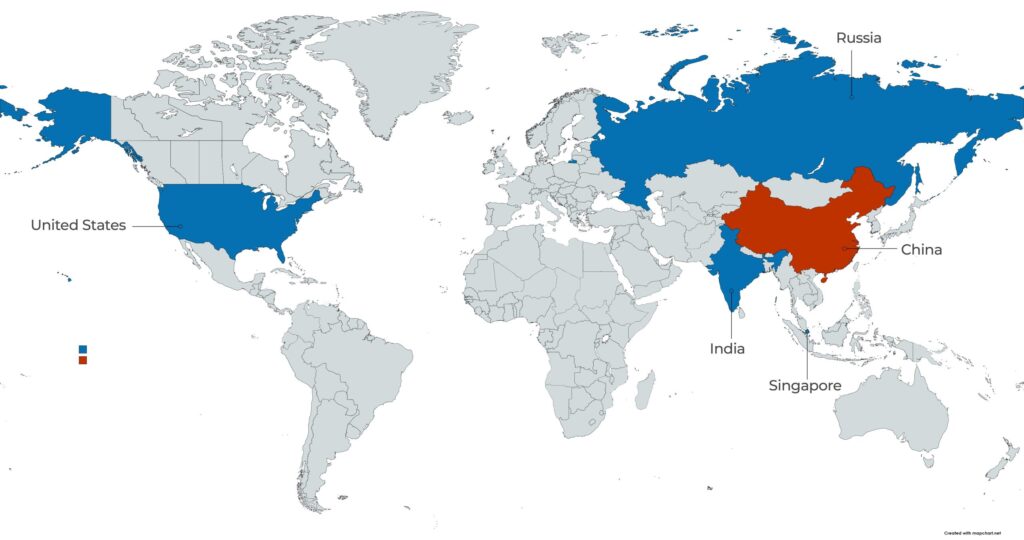
Russia remains the leading producer of natural industrial diamonds, contributing 18 million carats in 2023, or 41% of global production, while China and India are emerging as dominant players in lab-grown diamond production. About 50% of mined natural diamonds are suitable for jewelry, with the rest used for industrial purposes, whereas lab-grown diamonds are rapidly gaining traction due to their ethical, environmental, and cost advantages
After being bought by manufacturers, rough diamonds go to cutting centres where they are carefully inspected to decide how they should be cut to get the most value.
So what are the main factors considered while planning to cut a diamond? The first decision to be made is whether the diamond will be round, oval, pear, etc. Then, the proportioning of the facets and quality of the cut is planned using computer simulations.
After the size and shape of the stone are decided, taking into account the shape of the rough, as well as the amount and location of its internal inclusions, the process of diamond cutting begins. Diamond cutting is the practice of changing a diamond from a rough stone into a faceted gem. Cutting diamond requires specialized knowledge, tools, equipment, and techniques because of its extreme difficulty. The stone is marked and usually sawed/ cleaved.
Cleaving is the separation of a piece of diamond rough into separate pieces, to be finished as separate gems, while sawing is the use of a diamond saw or laser to cut the diamond rough into separate pieces. Since diamonds are made of the hardest material in the world, only a diamond can be used to mechanically cut another diamond. Lasers are another option for cleaving and bruting purposes. Usually, the tools used in the workshop consist of diamond-bladed edges or discs that are coated with diamond dust.
After the diamond is split, bruiting is then done to make the separated rough stones round. In the modern era diamonds are rounded using either a laser; a diamond disk covered with diamonds; or two diamonds cutting against each other. Industrial diamonds can also be used for bruting a diamond round.
Diamond polishing is the final polishing of the diamond. Once the round shape of the rough is formed, the next step is to create and form the facets of the diamond. The cutter places the rough on a rotating arm and uses a spinning wheel to polish the rough. This creates the smooth and shiny facets on the diamond. In a diamond factory one would find a diamond “Crossworker” who first places the main facets on a diamond (blocking the diamond).
This is done to ensure optimal weight, clarity and angles for the specific diamond shape. After the initial crossworking is done, the diamond is refined by polishing the main facets by the crossworker, which is called polishing the diamond. After the crossworker has polished the main facets, the final facets are added to the diamond by a “Brillianteer.” The facets that are added are the stars, top and bottom halves also called upper and lower girdle facets.
The last step of the diamond making process involves cleaning the diamond thoroughly in acids, and checking the diamond to see if it meets the quality standards of the manufacturer. If necessary, the stone would be returned to the polishers for some improvement if it didn’t meet the quality control standards.
After the diamond is made, diamond manufacturers sell the cut diamonds to jewellery manufacturers and wholesalers, who then sell these to jewellery shops and retail stores.
However, recently, due to the growing use of internet and technology, there have been changes in the diamond market as well with the diamond manufacturers now being able to reach the end customers directly. This has therefore made it possible to buy the same quality diamond for a much lower price.
Lab grown diamonds are becoming more popular in India for several reasons:
The government is investing in research and development to advance LGD manufacturing technologies. For instance, in the Union Budget 2023, a five-year research grant was allocated to the Indian Institute of Technology Madras to encourage indigenous production of LGD machinery, seeds, and recipes.
LGDs are considered more environmentally friendly and ethically sourced compared to mined diamonds. By promoting LGDs, the government addresses concerns related to environmental degradation and ethical issues associated with traditional diamond mining.
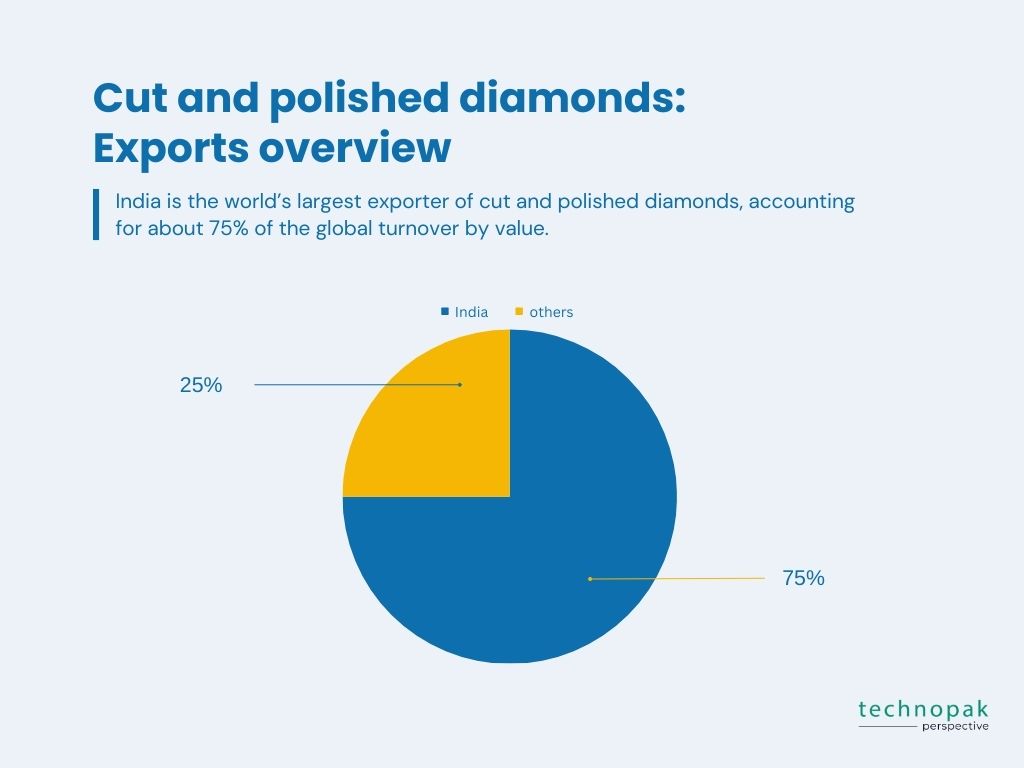
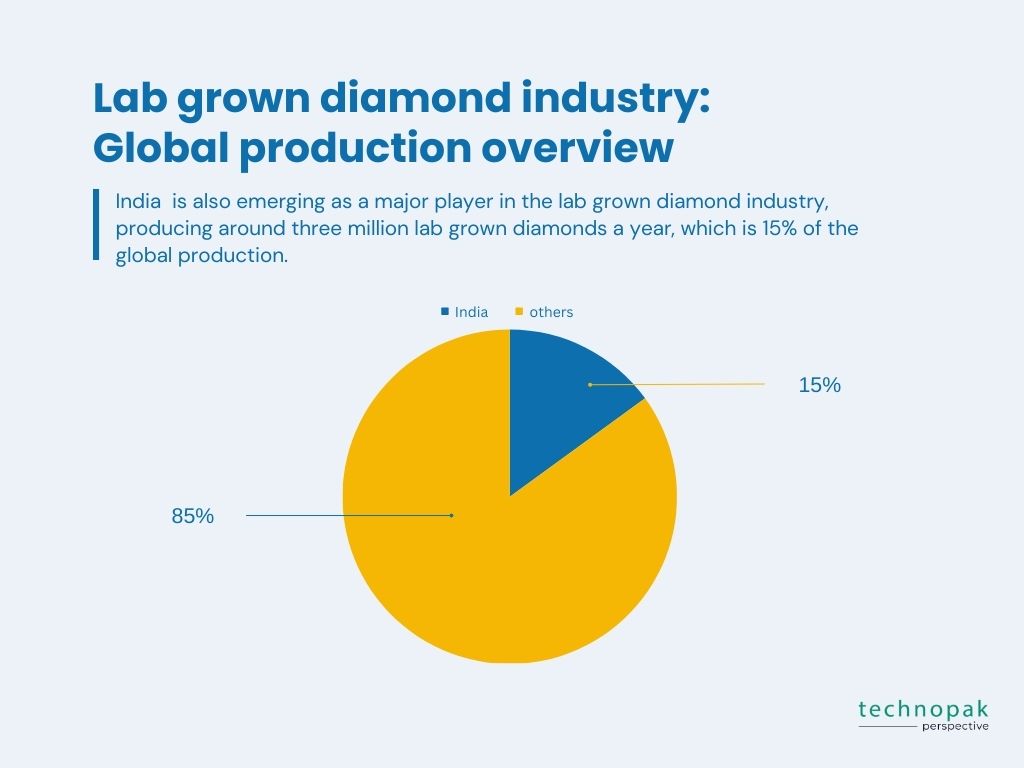
The country is also emerging as a major player in the lab grown diamond industry, producing around three million lab grown diamonds a year, which is 15% of the global production.
India has the advantage of having a skilled and experienced workforce, a well-established infrastructure and a strong domestic and international demand for diamonds.
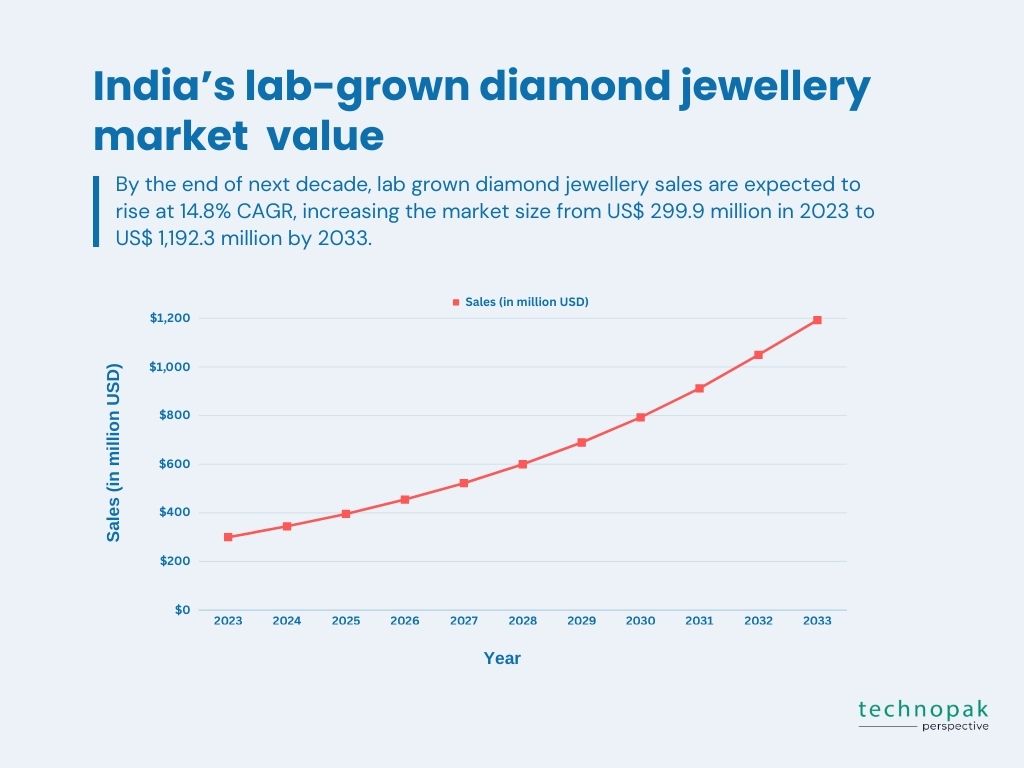
India’s lab grown diamond exports amounted to $1.05 billion from April 2021 to January 2022, which is a significant increase from the previous year.
India’s lab grown diamond industry is expected to grow further in the coming years, as more consumers and retailers embrace this new and exciting alternative to natural diamonds.
This price reduction, coupled with the ethical and sustainable appeal of lab-grown diamonds, attracted a diverse customer base, including high-net-worth individuals. The market’s expansion was further supported by the launch of new collections and showrooms, such as Firefly’s affordable lab-grown diamond jewelry line introduced during Diwali 2024.
Even high-net-worth individuals (HNIs) have taken a shine to lab grown diamonds, which prompted listed players like Senco Gold & Diamonds to enter the market in this financial year.
Even high-net-worth individuals (HNIs) have taken a shine to lab grown diamonds, which prompted listed players like Senco Gold & Diamonds to enter the market in this financial year.
Globally:
This almost doubled the calculations that had been made in 2021.
He also predicted that the total annual sales of jewelry with lab grown diamonds would reach $12 billion in 2025, which means that lab grown jewelry has exceeded 10% of the global diamond sales.
The larger man-made stones represented most of this rise.
The 3 to 3.50 carat range showed a 194% increase in gross sales and a 114% increase in volume.
The 4.50 to 5 carat range peaked with outstanding 582% increase in gross sales, while the 5.50 to 6 carat category grew by 78%2.
Therefore, it can be concluded that lab grown diamonds are the future of the diamond industry, and India is at the forefront of this revolution.

As of February 2025, the lab-grown diamond industry in India has seen significant growth, with several new players entering the market alongside established companies. Here’s an updated overview:
Craft Diamonds: Located in Mumbai, Craft Diamonds focuses on lab-grown diamonds and jewelry produced using the CVD method. Their brand, Craft Lab Grown Diamonds, features a collection of contemporary and classic designs.
Other significant producers include India, Singapore, Russia, and the United States.

Gold jewellery is considered auspicious and a symbol of wealth and status.
The yellow metal is also seen as a form of financial security and investment, especially in rural areas.
The precious metal also has a long history of holding its value and acting as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
Diamond, on the other hand, is subject to subjective valuations based on various factors like cut, clarity, color, and carat weight.
The resale value of diamond jewellery is often lower than its retail price due to factors such as market demand and the presence of middlemen in the diamond industry.
Gold jewellery also caters to different tastes and preferences across regions and communities in India.
Diamond jewellery, on the other hand, is more limited in its scope and appeal, and may not suit the diverse and dynamic needs of Indian consumers.
If you are a retail firm, a beauty or fashion organization or are looking for any advice on current trends, your own operations or business acceleration, Technopak is a market leader is advisory services.
Technopak has a proven track record of delivering successful outcomes for its clients across various retail segments such as fashion and lifestyle, food and grocery, electronics and appliances, home and furniture, etc.
If you are interested in learning more about retail consultancy or hiring a retail consultant for your business, please contact us.
Our team consists of skilled and experienced retail consultants who can assist you in transforming your retail business with expert guidance and solutions.